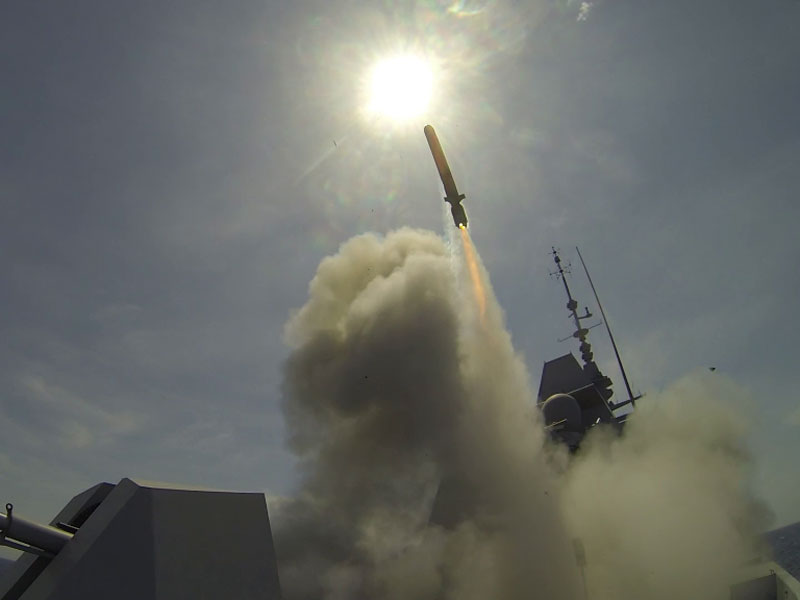
The two synthesis firings prepared by the crew of the French Navy, the DGA teams and manufacturers MBDA and DCNS are part of the verification of the technical capabilities of the FREMMs before entry into active service. This is another major milestone, after the firing of an Aster 15 anti-aircraft missile in 2013 and the commissioning on March 13 of the MU 90 lightweight torpedo on the Caiman marine helicopter, the naval version of the NH90 helicopter.
Future backbone of the French Navy, the FREMMs are heavily armed warships, carrying naval cruise missiles, Exocet MM40 anti-ship missiles, Aster anti-aircraft missiles and MU90 anti-submarine torpedoes. All the FREMMs can accommodate a Caiman marine helicopter, as well as Special Forces and their equipment. Six FREMMs will be delivered before mid-2019.
The naval cruise missile provides deep strike capabilities within enemy territory. With a range of several hundred kilometers, the naval cruise missile is capable of destroying infrastructure targets of high strategic value.