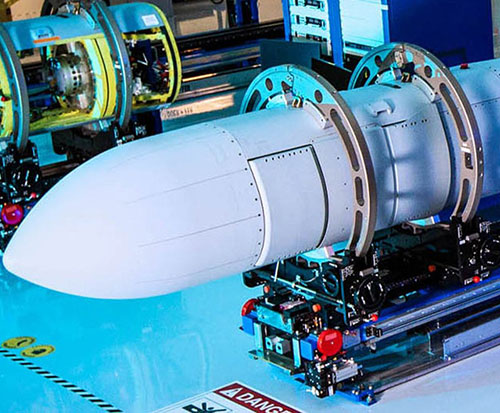
Raytheon Company was awarded a $403 million System Demonstration Test Articles (SDTA) contract with the U.S. Navy for Next Generation Jammer Mid-Band. The SDTA pods will be delivered to the fleet once developmental and operational testing is complete.
“These test assets will be used to show NGJ-MB is ready for operation. We’re at the stage where testing is essential. The test program is on target to meet Initial Operating Capability in 2022,” said Dan Theisen, Director at Raytheon Electronic Warfare Systems.
NGJ-MB provides significantly improved radar and communication jamming performance and capacity, as well as improved reliability and maintainability, for EA-18G Growler crews. Commanders will use NGJ-MB to deny, degrade and deceive the enemy’s use of the electromagnetic spectrum through advanced jamming techniques.
Raytheon delivered the first NGJ-MB pod to the U.S. Navy for testing in July of 2019.
Raytheon also announced it will help the U.S. Air Force modernize its missile warning architecture with a new system that will collect and fuse data from an array of sensors to provide a comprehensive picture of launch activity under a 5-year, $197 million contract.
To help with this mission, Raytheon Intelligence, Information and Services has developed a completely open framework - which the Air Force calls the Future Operationally Resilient Ground Evolution (FORGE) Mission Data Processing Application Framework (MDPAF) - that will be capable of processing Overhead Persistent Infrared (OPIR) satellite data from both the U.S. Air Force’s evolving Space Based Infrared System (SBIRS) constellation and the future Next Gen OPIR constellation, as well as be capable of processing data from other civil and environmental sensors.
“The U.S. government's global satellite network produces a constant flood of data - petabytes and petabytes of it every day. The Air Force wants to open that network up so they can use as much of that data as possible. That's a huge transformation not just for the service, but for the whole government,” said Dave Wajsgras, President of Raytheon IIS.
This is a significant departure from previous satellite ground control programs. Typically, companies would develop a system that collects and exploits data from specific types of satellites or sensors. FORGE changes this model as it’s able to collect data from nearly any type of satellite or sensor, and then helps operators make sense of that data quickly.
“Essentially, this is a smartphone model. We’ve built an operating system that everyone can build applications for – from Raytheon to the Air Force to universities to small companies. These applications allow the system to process specific types of data,” Wajsgras added.
One of the key benefits of incorporating new applications is that the system can be used beyond its intended mission. For example, an application could be built that would allow civil agencies to use the same satellite data to help detect forest fires, volcanic activity, agricultural changes, even surges in electric power consumption.
Further departing from the traditional ground control development model, Raytheon built the prototype system in less than a year and it’s capable of processing real data today. The company leveraged development work on several past programs, especially its Advanced Weather Integrated Processing System, to design the framework. Raytheon also developed applications using DevSecOps and Agile software development processes to dramatically speed development.
Raytheon will work with the Air Force over the upcoming years to further evolve and prove the framework’s capabilities.
Raytheon Company, with 2018 sales of $27 billion and 67,000 employees, is a technology and innovation leader specializing in defense, civil government and cybersecurity solutions.
With a history of innovation spanning 97 years, Raytheon provides state-of-the-art electronics, mission systems integration, C5I™ products and services, sensing, effects and mission support for customers in more than 80 countries.